Dependency inversion principle (DIP):
- High-level modules should not depend on low-level modules. Both should depend on abstractions.
- Abstractions should not depend on details. Details should depend on abstractions.
Example:
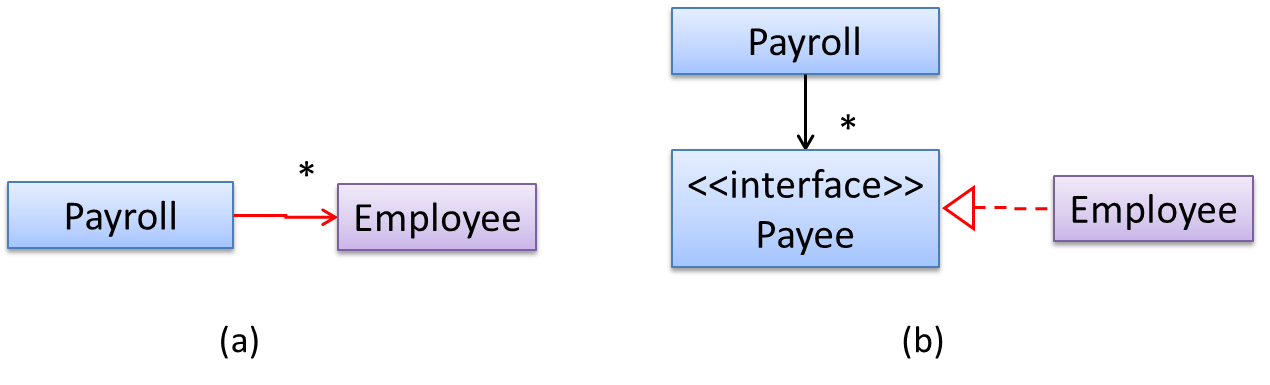
In design (a), the higher level class Payroll depends on the lower level class Employee, which is a violation of DIP. In design (b), both Payroll and Employee depend on the Payee interface (note that inheritance is a dependency).
Design (b) is more flexible (and less coupled) because now the Payroll class need not change when the Employee class changes.